Home medical devices are becoming increasingly accessible and affordable, allowing more buyers to enjoy the benefits of modern medical technologies. Being familiar with these various machines is the first step to taking advantage of their potential advantages. Those suffering from consistent pain may want to consider using a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) unit.
A TENS unit is a small device that emits electric impulses to electrode-embedded wearable pads. It is designed to help relieve sensations of pain and discomfort in users, especially those who suffer from arthritis or sports-related injuries.
This article will discuss what a TENS unit is, including what components it entails, what it can be used for, and what to look for when shopping for one. We’ll also address how these machines operate, how to use one, and potential safety hazards and concerns to be aware of.
What Is a TENS Unit?
A TENS unit is often a small, handheld electronic device that consists of several components. Still, no matter how a TENS unit looks or what its exact features happen to be, its purpose remains the same: Relieving muscle and joint pain by administering electricity to specific regions of the body.
Parts of TENS Unit
Though every unit is unique, they do all share a standard set of components and parts. Nearly every TENS unit consists of:
- A control unit.
- A display screen.
- Electrode inputs.
- Electrode pads.
- A battery or charging cable.
While additional accessories and materials are a fantastic plus, they’re not necessary.
Control Unit
The control unit is what powers the rest of the device. It typically houses the display screen, electrode inputs, and battery compartment or charging input. These units range in weight between one and two pounds and are often designed to fit comfortably in the palm of your hand. Some may feature aesthetically pleasing glass faces, but be aware that these models can shatter when dropped. A rugged design that features a deep-set screen is preferable for those who are prone to the occasional bout of clumsiness.
Display Screen
A TENS Unit’s display screen should allow users to view important information, such as battery level, timer amount, mode setting, and frequency. Of course, a display’s usefulness and attractiveness are bound to vary from user to user, as some may only need a few programs or options, while others may desire to have tons of pre-programmed modes.
It’s important to note that while most TENS units do feature backlit display screens for easy evening reading, some do not. If having a lit screen is essential to you, be sure to double-check for this feature before making your final purchase.
Electrode Input
No matter the exact type of electrode pads the user wears, they’re bound to feature a cable adapted that fits neatly into the control unit’s electrode input. Dual-channel devices will have two electrode inputs, allowing the user to treat multiple areas at once.
Electrode Pads
Electrode pads come in many colors, sizes, shapes, and styles, but their primary purpose is consistent. They allow electrical impulses to travel from the control unit to the user’s body, and they’re often covered in an adhesive to keep them from slipping during use.
While most will have no adverse reaction to using standard electrode pads, some may experience an allergic reaction to latex-based pads, and should, therefore, opt for a hypoallergenic alternative. In addition, it’s relatively common for users to experience slightly reddened skin after using a TENS unit, though this is likely due to increased circulation.
Still, if you experience dry, itchy skin or a rashy area after applying a TENS electrode pad, wash the affected area in lukewarm water and mild soap for several minutes, then pat dry. Do not reapply the pads, and be sure to call the manufacturer for more information regarding treatment. If you experience a painful burning sensation, it may be best to seek immediate medical attention.
Battery/Charging Cable
Non-rechargeable units need batteries to function, whereas rechargeable TENS units only require a power source. Battery-powered units tend to be less expensive but have fewer features when compared to their rechargeable counterparts. However, they are just as long-lasting and effective as rechargeable models.
What Is a TENS Unit Used For?
A TENS unit is primarily used to help users lessen their perception of pain, in turn helping them to live more fulfilling lives. It is often used to help alleviate:
- Joint pains.
- Menstruation aches and pains.
- Labor pains.
- Back pains.
- Shoulder pains.
- Pain-related to postoperative care.
However, TENS units also have several more potential uses that are still being studied. These additional uses are yet to be thoroughly verified by the professional medical community. Still, they will likely either be approved within the next few decades as more information develops.
Want to know where a TENS unit can be placed? Check out my TENS placement guide here
Generalized Pain Relief
A TENS unit can help reduce sensations of pain almost immediately and can help quell those sensations for several hours. That’s why these devices are popular among those with:
- Osteoarthritis.
- Chronic lower back pain.
- Tendinitis.
- Fibromyalgia.
- Diabetes.
- Bursitis.
- Labor contractions and pain.
Nerves are located all throughout our bodies, and they’re responsible for sending pain signals to the brain. By applying electrical impulses to pain-generating nerves, you can potentially reduce negative sensations and regain a sense of wellness and vitality.
How High Should I Set My TENS Unit? click here to read what settings to use.
Why should you trust me?
I have exTENSively used TENS units for neck, shoulder, back and knee issues and became familiar with TENS therapy through countless visits to my chiropractor and physical therapist’s office. I have spent many hours researching and reading how TENS therapy can alleviate pain.
I consider myself knowledgeable in the use of TENS units and have used them regularly to help manage pain over the years. Many of my recommendations are from firsthand experience/use and hopefully my information can be a benefit to you.
Additional Potential Uses
Though these uses are still being studied, there is some initial evidence to support that a TENS unit could become more useful in treating a wide variety of ailments. There are several illnesses and conditions that TENS may be able to help treat, including:
- Depression and mood disorders.
- Recurring migraines and headaches.
- Pain relating to symptoms of PMS.
- Post-stroke recovery.
- Lung function and strength.
Still, these claims have yet to be fully verified and should be considered as only potentially helpful.
Features to Look For in a TENS Unit
Before investing in a TENS unit, you’ll want to keep several critical factors and features in mind. A great place to start is to recognize what you intend to use the unit for. For example, if you’re interested in after-work TENS massage or acupuncture programs, you’ll likely be more inclined to purchase units that have a vast selection of those types of therapies.
However, if you’re more interested in getting a TENS unit for upcoming labor pains, you’ll be looking for something small, powerful, and easy to use. It might also help to choose a unit that can go from off to ready in several seconds.
Once you’ve recognized your intent, you can begin examining useful product characteristics and features. When you’re familiar with these aspects, you’re bound to make a better, more informed purchasing decision.
Need a TENS Unit?
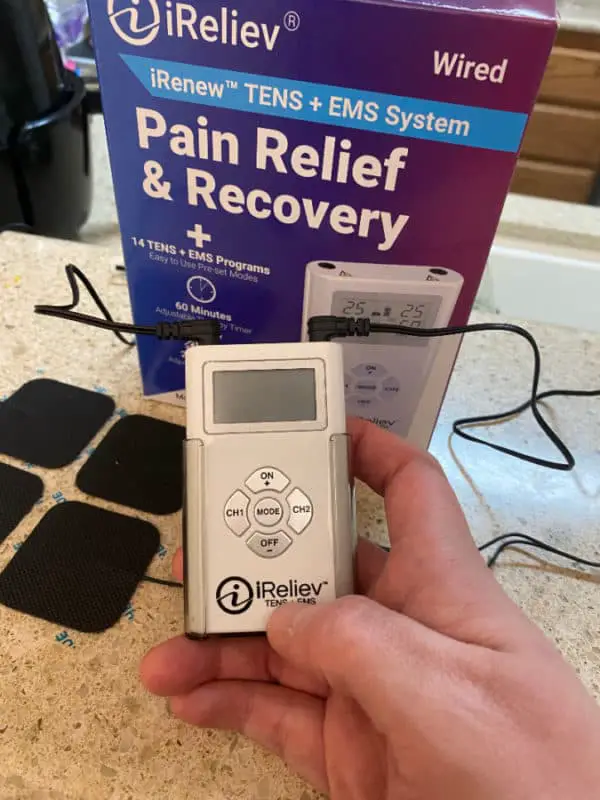 This is the exact TENS unit that I use. It is perfect for alleviating many common types of pain. The iReliev is a great little device and has a lot going for it. It is well under $80 and has several programs to choose from and is small enough to fit in your pocket.
This is the exact TENS unit that I use. It is perfect for alleviating many common types of pain. The iReliev is a great little device and has a lot going for it. It is well under $80 and has several programs to choose from and is small enough to fit in your pocket.
You do not need to spend hundreds of dollars to get a quality TENS unit and iReliev gives you a ton of value for the price being paid. Best part is they are based in Dallas, Texas and have phenomenal customer service FREE shipping and delivery in less than 5 days.
Get yours today on the iReliev website by clicking here.
Battery Type
All sorts of different batteries can power a TENS unit. Some sport heavy 9-volt batteries, while others hum along on dual AAs. Still others calmy operate off a lithium battery’s charge and are easily rechargeable. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, but if you’re looking for the longest-lasting battery, you’ll definitely want to opt for the lithium models.
Battery Life
Removable batteries can last anywhere from several weeks to several months, depending on how often the user operates the unit. However, a rechargeable model can last for two or three years before kicking the bucket.
The main difference between these two lies in control unit longevity. For example, when a unit with removable batteries powers down, you can replace the batteries and the unit will simply boot back up. But when a lithium battery dies for the last time, there’s no bringing it back. You’ll have to chuck the entire unit and buy a replacement.
It’s not hard to figure out that the more wallet-savvy option is the replaceable battery model, as the cost of replacement batteries will almost always be less than the cost to replace an entire unit, even after two or three years.
Programs and Modes
It’s not uncommon to find a TENS unit with multiple modes or programs. These are either designed to be used on specific areas of the body or they are imitations of traditional massages or physical therapy treatments. Potential users looking for a deep-acting massage tool may want to consider a model with a greater variety of programs and modes.
Timer
Setting a timer on a TENS unit is simple, and it can help users ensure that they receive the correct amount of stimulation. Most devices allow for ten-minute increments, starting with ten minutes and allowing for an hour of therapy at the most. An additional benefit to timers is convenience. You can set the time, press the start button, and forget about it.
Intensity Levels
Most modern handheld units have an intensity adjustment, whether it be a twistable dial or pushable button. Intensity and TENS effectiveness go hand-in-hand, so it’s vital to invest in a unit with multiple intensity settings. In addition, varying your intensity level to match your level of pain could increase your therapy’s effectiveness.
Ease of Use
It’s vital to choose a unit that is easy to operate. Otherwise, you may have the best, most effective TENS unit in the world but never get to enjoy its benefits. It may be better to choose an alternative model if you find a particular unit’s display screen overcomplicated or confusing.
Most importantly, a TENS unit doesn’t need to have an overload of features to be effective. Some of the most powerful and affordable models have very ‘extra’ benefits besides applying consistent, targeted electrical stimulus.
Affordability
The average TENS unit varies significantly in price and can cost anywhere between $25 and $100. While there are a few units that cost more than $100, they’re often just a single component of a much larger kit.
Included Equipment
Depending on the model, you may end up receiving just a control unit or a TENS unit kit. Some kits are incredibly affordable and very basic, while others are a bit more extravagant. In either case, it’s always wise to choose a unit that includes the following equipment:
- A control unit with a backlit display screen.
- Batteries or a charging cable.
- Four or more electrode pads. Multiple sizes are preferred.
- A user’s manual or operation guide.
Additional accessories are often practical, but they’re not entirely necessary. Still, if you’re looking to gift a TENS unit (to someone else, or yourself), it may be worthwhile to spring for the attractive extras.
Multi-Functionality
It may be worthwhile to invest in a multifunctional TENS unit, namely a TENS/EMS device. These machines are capable of providing both TENS therapies and treatments and EMS therapies and treatments, making them some of the most multifunctional stimulus devices available.
However, many novice users are unaware of the difference between these two systems, which can prove confusing. It may also make the purchasing process more difficult, as many EMS and TENS units are sold interchangeably.
What is the Difference Between a TENS and an EMS unit?
Several popular TENS units are TENS/EMS units. This may leave you wondering how a TENS unit differs from an EMS unit, and if it’s important. Let’s explore how these two types of devices differ, and what it means to the person using them.
Firstly, TENS units and EMS devices work in the same way. Both emit electrical signals and impulses to electrode pads. The difference lies in the frequency of the pulse and the resulting action.
TENS units are designed to target nerves and block their ability to send pain signals to the brain. In many cases, they must be able to reach deep beneath the muscle tissue to affect these nerves, so they tend to be reasonably powerful. Individuals with chronic, painful conditions (like arthritis) can find temporary, consistent relief with a TENS unit.
On the other hand, an EMS device can help individuals heal, tone, and strengthen muscle tissue. The electrical current produced by these machines causes the skin and muscle beneath the electrodes to contract, stimulating improved circulation and muscle growth. Anyone with muscle atrophy, sore muscles, or tense muscles can enjoy the healing and relaxing effects of an EMS device.
Because these systems both rely on the same basic output (an electrical signal), it’s common to find them as singular devices. Admittedly, it’s advantageous to own a TENS/EMS unit, as it allows for a greater range of functionality.
How Does a TENS Unit Work?
Now that you know what a TENS unit can do, what it consists of, and what features to look for in a new device, it’s time to address how it works. While it’s important to consider the operational aspect of how a TENS unit functions, it’s just as crucial to discuss how it relieves pain.
Electricity, Nerves, and Pain
The nervous system is an incredibly complex biological system that extends throughout the entire body. The ‘main hub’ of this system is the brain, which processes signals from the bodywide nerve endings to make life-saving decisions. Many of these decisions are unconscious, reflexive processes, including the sensation of pain.
Signals travel along nerves via small, electrical currents. The goal of a TENS unit is to temporarily interrupt specific electrical signals to prevent pain signals from reaching the pain and manifesting as an unpleasant sensation. However, there’s still very little information on how a TENS unit achieves this precise result. Still, there are two prevailing theories.
Theory One: Gate Control
The Gate Control theory posits that electrical stimulation can close specific ‘signal gates’ along the spinal column, preventing pain signals from reaching the brain. This theory essentially purports that TENS units overload the sensory response system, temporarily disabling the body’s ability to sense pain.
Theory Two: Endorphin Release
Alternatively, there’s the Endorphin Release Theory. In this theory, the TENS unit supposedly induces a euphoric, pain-relieving effect in users by encouraging the brain to produce and release sizable amounts of endorphins. These hormones are often released during exercise, periods of extreme stress, or while laughing. They can reduce our perception of pain, albeit only temporarily.
The Bottom Line
There is no single consensus for how a TENS unit is able to quell sensations of pain, and trials and tests are still ongoing. Yet, based on the amount of current evidence and consumer feedback, it seems evident that no matter how TENS units do their thing, they do it exceptionally well.
How to Operate a TENS Unit
Using a TENS unit is incredibly easy, and the step-by-step process tends to be similar no matter which model you have. Still, it’s essential to read the owner’s manual or manufacturer’s guidelines before getting hands-on with your unit.
Always Read the Manual
A quality TENS unit will always come with instructions for use. While some companies may choose to host virtual manuals, the site address for these types of guides is often included within the unit’s packaging. Reading the instructions is vital because most manufacturer’s guides will contain specific information regarding usage, setup, and device hazards.
Place the Electrodes
Most TENS electrode pads come with a sticky adhesive layer protected by a thin, peelable layer of plastic. If you’re allergic to latex or common adhesives, you may want to purchase separate, hypoallergenic pads that are adhesive-free. You can also find skin-friendly adhesive options for many electrode pads.
After peeling away the protective plastic bottom layer, place the pad on above, beside, or next to the area you intend to treat. Secure the pads by firmly pressing down on their sides for several seconds. Ensure that you’re placing the electrodes in appropriate locations. Your unit’s manual may have helpful pictures to help you through this part of the process.
Connect the Adapters
After placing the electrodes, it’s time to connect the adapters. Each electrode should end with a short metal adapter that fits neatly into the control unit. Be sure to fully depress the adapter when inserting, ensuring that it has a full connection with the unit. Now you’re ready to power the control unit up.
Turn the TENS Unit On
Some models may have an ON/OFF switch, while others have a pressable button. Whichever mechanism your model employs, go ahead and power the unit on. The display screen should immediately become visible, and you should be able to select various menus, features, or settings. If you own a TENS unit with a backlit screen, you won’t even need to get up and turn on the lights for this step.
Set the Unit to Desired Settings
The exact sequence of settings differs from model to model, but the general idea remains the same. After powering the TENS unit on, users will need to select their preferred treatment settings. Some units may allow you to adjust the frequency of the signals, or their pulse width. Others will give you a dozen or more pre-programmed therapy options from which to choose.
Occasionally, the iconography used to represent different modes can be confusing. Always consult your user’s manual to discern the exact program or mode you’re selecting before hitting the start button. Also, be sure to examine and adjust the intensity level. While you may require a higher intensity therapy on days when you experience high levels of pain, you may not need the same level of intensity of calmer, more restful days.
Enjoy Your TENS Therapy
Before starting your program, timer, or mode, double-check to ensure that your:
- Electrode pads are firmly secured and appropriately placed.
- Timer is set to the correct amount.
- Intensity is set to a safe level.
- All connections are complete, and adapters are fully inserted into the control unit.
Now, simply press the play or start button on your device, relax, and enjoy the benefits of TENS. Be sure to stay awake, and though it may be tempting, never use a TENS device (or any other electronic device) while bathing.
Potential Hazards and Safety Concerns
Before investing in a TENS unit, it’s important to be aware of the potential hazards you may encounter. For example, a TENS unit can interfere with pacemakers, causing the artificial pump to fail or malfunction. This, naturally, is a dangerous situation for anyone who relies on a pacemaker for survival.
However, in addition to notable pre-existing conditions, interested buyers should also be aware of poor placement areas. While the majority of the body is incredibly receptive to TENS therapy, there are a few regions that are incredibly sensitive, and electrodes should never be placed on these body parts.
Pre-Existing Conditions
There are a few pre-existing ailments that preclude individuals from safely using a TENS unit. These include:
- Heart conditions or pacemakers.
- Internal electronic pumps or monitors.
- Pregnancy.
- Epilepsy.
Women who are in the process of giving birth are more able to safely use a TENS unit, as their infant’s development will be far less impacted by low-strength electronic signals. Also, individuals with epilepsy may be able to use a modified TENS unit to help reduce the instance of seizures.
Naturally, it’s imperative to consult with your physician before implementing any changes in your health care routine. They can help guide you in choosing the best solution for your specific condition, needs, and preferences.
Approved Placement Areas
Avoiding accidental TENS injury is simple, and most users can safely operate their device without any difficulty. Pain relief begins by placing the electrode pads on the:
- Entire back area, lower and upper.
- Wrists, elbows, and arms.
- Knee, legs, ankles, and feet.
- Hips.
- Thighs.
- Lower abdomen.
While some manufacturers may advertise usage for the chest, ears, or head, these areas are strictly off-limits when it comes to TENS electrodes. You should never apply your TENS unit to any of these areas when using the device.
Poor Placement Areas
While there are several excellent pad placement areas throughout the body, there are also a few poor ones. Users should never place an electrode pad on their:
- Eyes.
- Nose.
- Mouth.
- Ears.
- Neck.
- Head.
- Chest.
- Genitals.
Also, TENS unit electrodes should never be placed on an open wound, sore, or laceration. The same goes for areas that have recently received radiation treatment. If you’re ever in doubt about inappropriate electrode placement areas, you can do two things.
Firstly, you can consult the manufacturer’s directions and guidelines. Secondly, you can consult with your physician. Both routes are bound to lead you in the right direction and help ensure that you’re always using your unit correctly and safely.
Conclusion
A TENS unit is an electronic device that may be able to help relieve pain. It’s particularly useful for those with sports-related injuries, muscle soreness, and arthritis. However, it has far more potential uses that will likely be explored within the next decade. When purchasing a TENS unit, there are several features to consider, but the ideal model for you depends on your budget, preferences, and needs.
There are a few precautions to take before using a TENS unit, and pregnant women or individuals with pacemakers should avoid TENS units, as the electric impulses they emit could cause significant harm to sensitive users. However, most will find TENS unit therapy completely safe and utterly enjoyable.
Sources
- Cleveland Clinic: Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
- Healthline: Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Unit
- MedicineNet: Endorphins: Natural Pain and Stress Fighters
- MedicalNewsToday: What is a TENS unit and does it work?
- myDoctor.com.au: TENS – transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Effectiveness of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation for Treatment of Hyperalgesia and Pain
- OMRON Healthcare: Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) vs Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)
- SelfHacked: 11 Interesting Uses of TENS Units for Pain Relief & More
- The University of Iowa: Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulator (TENS)
- WebMD: TENS for Back Pain
- Wikipedia: Endorphins
- Wikipedia: Nervous system
- Wikipedia: Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation




3 responses to “What Exactly Does A TENS Unit Do?”
[…] chronic pain, you would be better suited to visiting your doctor and getting a prescription. These units offer more settings so you can adjust the unit’s output to fit you exactly – rather than relying on preset functions in the OTC units. They also have the option to rent you […]
[…] specialists and family doctors early on before you give it a try. Under supervision, though, a TENS unit may be exactly what you were looking […]
[…] exists no consensus on exactly how TENS Units produce the sought after results. When it comes to the subject of pain relief most practitioners […]